FTL Features
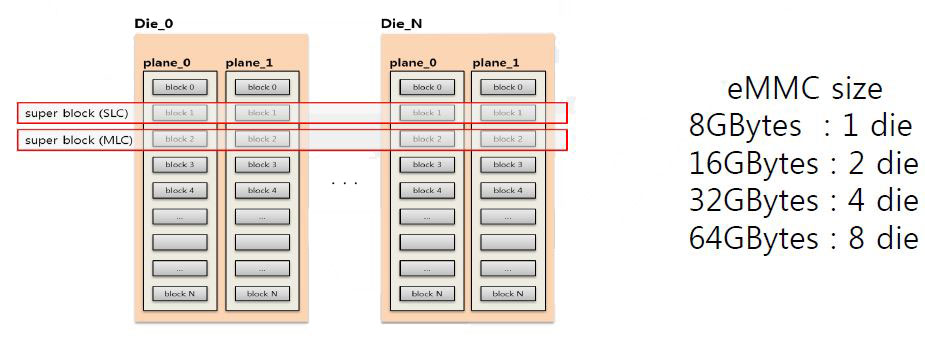
Super-block and SLC/MLC mode
- Super-block is necessary to use multi-plane cmds for high r/w speed
- Super-block is a group of same block
- Size of super-block is 16MB=4X4M for 2 die, or 32M for 4 die
- Every allocation is based on a super-block
- The mode (SLC or MLC) is selected at the super-block allocation
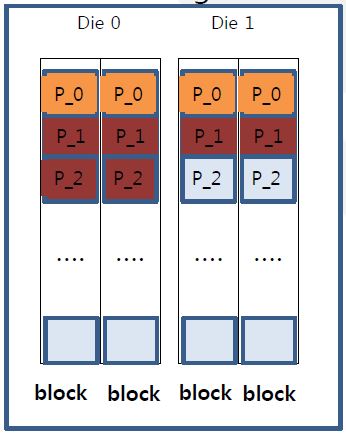
- Basic allocation unit of MLC log-buf is two pages
- MLC log-buf always uses multi-plane prog command for high speed
- Multi-plane program should use same page-number
- Write request sequence:
W_req_1 : 48KB=16KB x 3
W_req_2 : 70KB =16KB x 5
- W_req_1 : allocate 4 pages while skipping one page
- W_req_2 : allocate 6 pages while skipping one page
Log-buf Algorithm
- Based on write-req size, allocating user-data into SLC-log or MLC-log
- below 16K, go to SLC
- Over 16KB, go to MLC
- Basically, two logs for one SLC log and one MLC log
- However, four log is possible for two SLC logs and two MLC logs
- Actual consumed blocks is totally different with write patterns
| pattern | Traffic amount (Bytes) | Consumed SB | WA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128 times of 4K | 512K | 0.25 | 8 |
| 128 times of 16K | 2M | 0.25 | 2 |
| 256 times of 20K | 5120K | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| 256 times of 32K | 8192K | 0.5 | 1 |
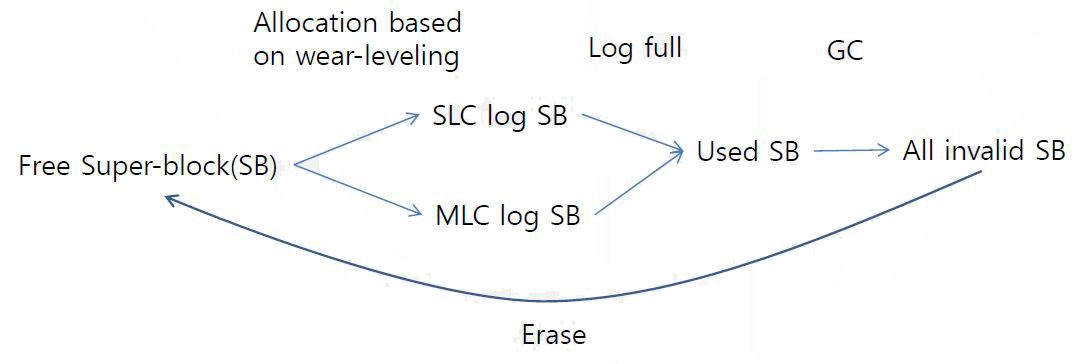
SB life-cycle
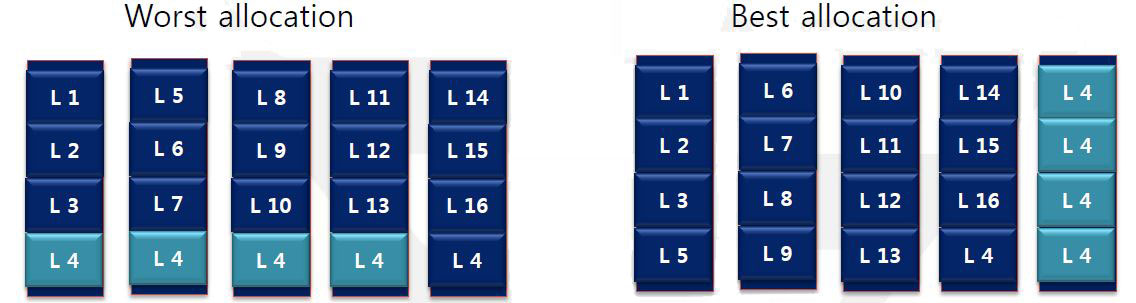
Allocation algorithm
- Write sequence
- Logical address (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 4, 14, 15, 16, 4)
- GC Cost
- 12 page copies and one erase V.S. one erase
- In case of 256 pages, Write amplification 255 V.S. 1
- Hot/cold Awareness is important
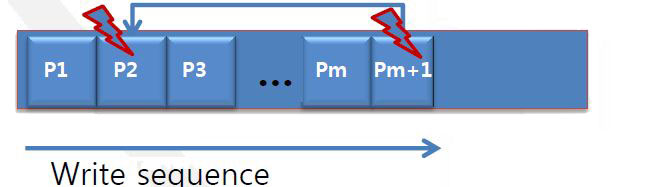
Paired page issue
- a page programmed successfully can be broken if the following paired page is damaged by power-failure
- Damage of Pm+1 crashes P2’s content which is programmed successfully
- =>Solution : backup P2 before Pm+1
- Solution
- before starting programming Pm+1, the paired page, P2, is copied to temporal buffer
- The temp buffer should be scanned at booting to recovery P2’s content if that is crashed
- Write request for Pm+1 arrives
- Copy the paired page into temporal SLC block
- Program Pm+1
Simple full page map
- Every Logical block(LB) has an physical page address(PPA)
| Element | Size (Bytes) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Nand page | 16KB | |
| Logical block | 16KB | |
| Total number of map element | 2048KB | 32GB /16KB |
| Size of map | 8192KB | 4Bytes X 2048K |
| Total number of pages for map | 512 ea | 8192KB/16KB |
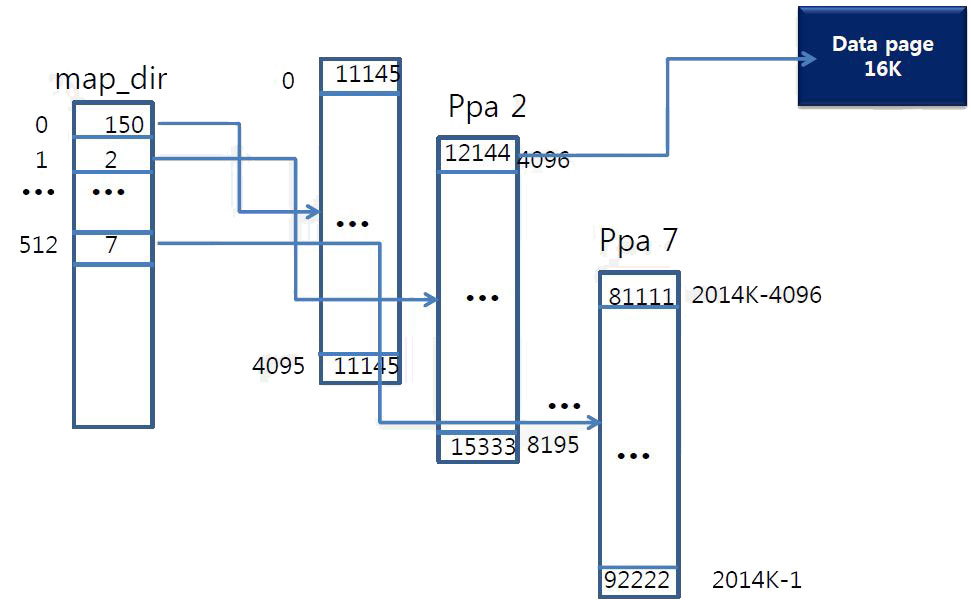
Map-table structure
- Map_dir
- Map_page 1)Write request for 4096 LB arrives 2)Lookup map_dir & get ppa 2 for map_page 3)Lookup map_page & get ppa 12144 for data
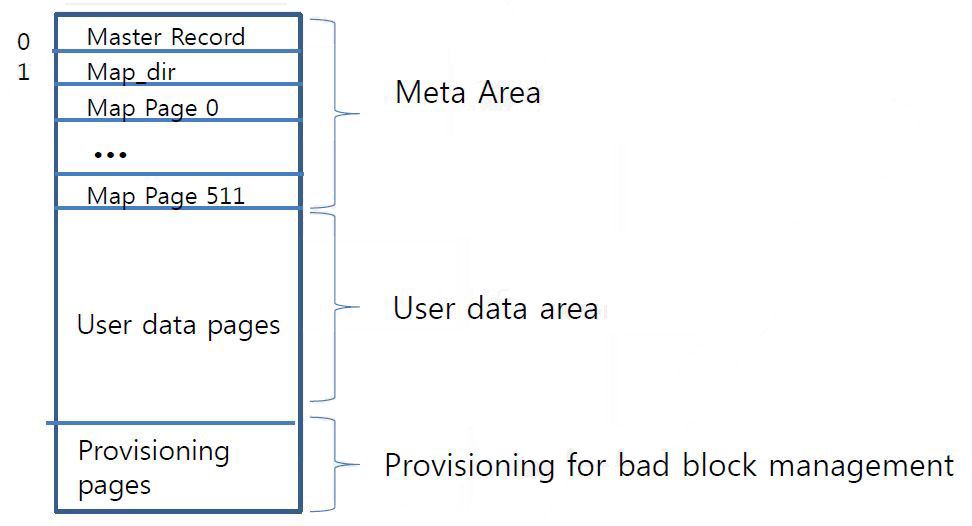
NAND Area Partition
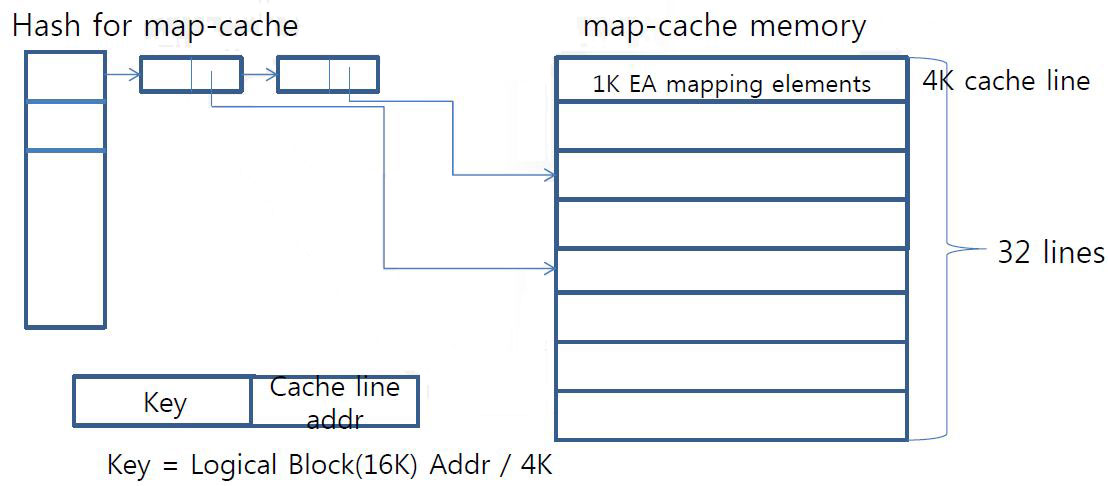
Map cache
- SRAM of eMMC is too small for all map
- SRAM is around 256K and consumed for (code, data buffer, map)
- SRAM for map is under 128K
- Map-cache is SRAM area to keep small part of the entire map-table
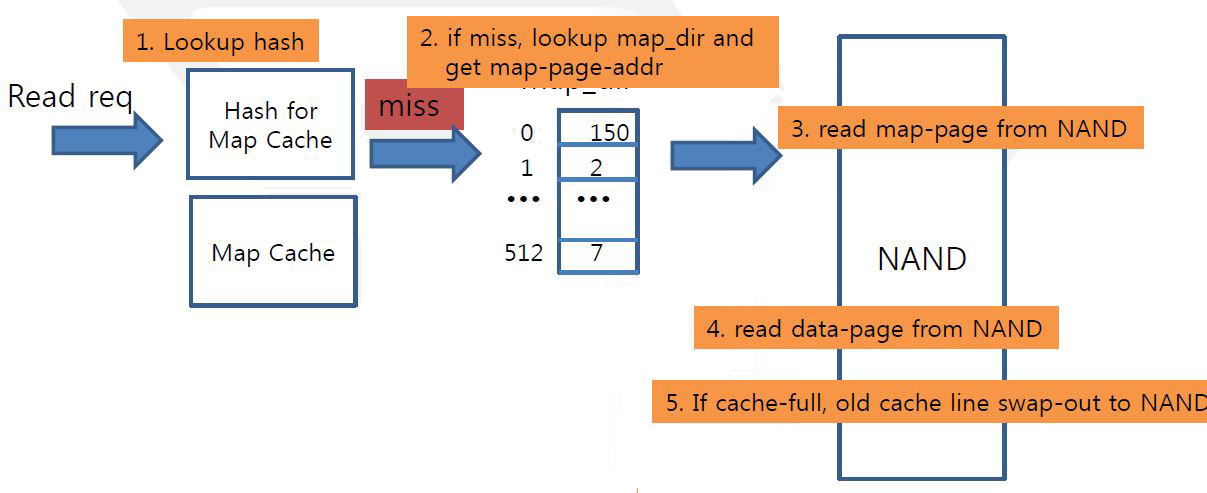
Read Sequence
Worst cases : frequent map-update
- Cache-line is 4K bytes which contains 1K ea mapping info
- covering 16M logical area (1K X 16K page)
- Writes sequences
- Page 0, page 1K, page 2K, … , page
- Update map-page into NAND per writing every pages
- Programming 2 NAND pages for each 1 page write request