IO Scheduler
The I/O Scheduler is designed to perform the Disk I/O efficiently. In kernel 2.6.10, there are four type of noop, cfg, deadline, anticipatory, default is cfg.
The key factors in determining the IO Scheduler Design within OS is throughput vs latency (response time )
The I/O Scheduler maximizes the global throughput by minimizing the seek time by manipulating the Request Queue appropriately. Tow basic operation of merging and sorting are used here. That is, When a request arrives, it joins two request when there is already in the queue or a request for a neighboring block. Also, to reduce disk seeking, the new arriving request is inserted into request list, not to append that to the already waiting block list as FIFO method according to block number. This minimize the disk seeking and allows the arm of disk to be serviced while traversing the disk.
However , there should not be many “starving I/O requests”. keep fairness fairly, and reduce the latency. This is simular to an elevator , so the I/O Scheduler is also called as elevator.
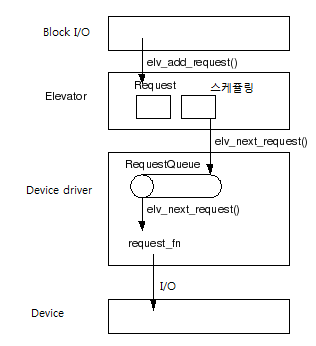
Block I / O Request Once put in the elevator, it is reserved and is dispatched. Requests to be dispatched are put into the RequestQueue and the device driver performs I / O.
What type of I / O Elevator?
1.noop
- No Operation. Scheduler that does nothing
- It is based on the idea that if you have a smart RAID controller, use an SSD, or use a good disk, such as a semiconductor disk, the scheduler is the chosen scheduler,
2.anticipatory(as)
- It estimates the location of future I / O requests in the generated I / O requests, stops processing I / O requests that have been dropped, and processes I / O requests that are close to the location.
- Reduce latency and improve throughput
- It is similar to a traditional hard disk.
- There is a possibility that the delay time will be bad due to the nature of collecting and processing input and output
3.deadline
- Prepare a deadline for I / O latency and process it first
- Scheduling optimized for latency rather than throughput
- Balance both reading and writing
- Some processes are suitable for environments that generate a large number of I / Os
- Used extensively in database file systems
4.cfq(Completely Fair Queuing)
- Each process has an I / O queue and reserves as much as possible
- Many processes can be used to generate a lot of fine I / O
- It is the base for the Fedora Core kernel package.